Use geotagged jpeg images as map backgrounds
Introduction
Sometimes we can obtain the best map background images in the form of georeferenced images, such as geoTIFF or jpeg. In this example we'll use a jpeg file downloaded from the excellent NearMap site (my university has a subscription 😊). Specialist mapping websites may have better resolution, or have aerial photographs from the most appropriate time of year for our mapping exercise.
First we load the packages that we need:
We should note that the jpeg file itself doesn't have
spatial information, even though we may have downloaded it as a
georeferenced image. With jpeg images, georeferencing comes in the form
of a companion ('sidecar') file, with the same name but having the
.jgw extension. We can read this directly, but the
functions we will use below will look for this file and use the spatial
information directly. The .jgw file has 6 lines:
- length of a pixel in the x direction (horizontal)
- angle of rotation (is usually 0 or ignored)
- angle of rotation (is usually 0 or ignored)
- negative length of a pixel in the y direction (vertical)
- x coordinate at centre of pixel in the top left corner of the image
- y coordinate at centre of pixel in the top left corner of the image
So long as the file names of the .jpg and
.jpw files match, the raster extent and coordinates are
obtained or calculated from the values in the .jpw
file.
Reading the raster spatial information in the georeferenced jpeg image
We use the stars package, which plays nicely with the
sf package, to do most of the work (the sf
package was introduced on another page on maps in
R. The read_stars() function will find
and use the information in the .jpw file without us
specifying that file explicitly.
## stars object with 3 dimensions and 1 attribute
## attribute(s), summary of first 1e+05 cells:
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## EPSG32750_Date20230226_Lat-... 0 85 143 139.6958 200 255
## dimension(s):
## from to offset delta x/y
## x 1 1267 399868 0.5972 [x]
## y 1 795 6468376 -0.5972 [y]
## band 1 3 NA NAWe notice that, apart from the long and informative filename, the
resulting stars object does not have a coordinate reference
system included, so we need to add the appropriate one manually:
## [1] "EPSG:32750" "PROJCRS[\"WGS 84 / UTM zone 50S"The messy output above shows that we have what we expect: UTM Zone 50 (south), based on the WGS84 datum.
From the summary of the read_stars() output above
(i.e. band 1 3), we can see that the image
has three bands of information, corresponding to the red, green and blue
colour channels in the jpeg image.
To plot as a combined colour image we need to merge these 3 channels
into in single data layer of colour information; fortunately, there is a
function for this in the stars package:
st_rgb():
## stars object with 2 dimensions and 1 attribute
## attribute(s), summary of first 1e+05 cells:
## EPSG32750_Date20230226_Lat-...
## Length:100000
## Class :character
## Mode :character
## dimension(s):
## from to offset delta refsys x/y
## x 1 1267 399868 0.5972 WGS 84 / UTM zone 50S [x]
## y 1 795 6468376 -0.5972 WGS 84 / UTM zone 50S [y]We need some data to plot, so let's read some
git <- "https://github.com/Ratey-AtUWA/cybloRg/raw/main/"
afs1922 <- read.csv(paste0(git,"afs1922edit.csv"), stringsAsFactors = TRUE)
afs1922$Year <- as.factor(afs1922$Year)
(afsREE <- st_as_sf(x = afs1922[,c("Year","Easting", "Northing","Al","Fe","REE")],
coords = c("Easting", "Northing"), crs = st_crs(32750)))## Simple feature collection with 262 features and 4 fields
## Geometry type: POINT
## Dimension: XY
## Bounding box: xmin: 399908 ymin: 6467930 xmax: 400577 ymax: 6468346
## Projected CRS: WGS 84 / UTM zone 50S
## First 10 features:
## Year Al Fe REE geometry
## 1 2019 8996 28836 25.74 POINT (399989 6468038)
## 2 2019 37131 44687 184.71 POINT (399981 6468037)
## 3 2019 28699 48561 161.33 POINT (399971 6468035)
## 4 2019 33882 53061 161.90 POINT (399958 6468028)
## 5 2019 31222 71546 166.20 POINT (399944 6468023)
## 6 2019 34765 38441 142.29 POINT (399930 6468017)
## 7 2019 27926 59783 129.82 POINT (399919 6468014)
## 8 2019 29650 37017 117.57 POINT (399908 6468006)
## 9 2019 17946 135488 71.19 POINT (399971 6468021)
## 10 2019 4114 9255 10.46 POINT (399981 6468052)Now we can plot a map with some data on it! We use the
image() function to plot the stars raster; we could also
use plot() if we specify the argument
reset = FALSE.
palette(c("white", mako(8, dir=-1, alpha=0.7), "black","transparent")) # custom palette
par(mar=c(3,3,1,1), oma=c(0,0,0,0), mgp=c(1.6,0.3,0), tcl=-0.2,
font.lab=2, cex.lab=1.2, lend="square", ljoin="mitre")
# Plot an empty frame, same size as the stars object
plot(matrix(st_bbox(AF_rgb), nrow=2, byrow=T), asp=1, type="n",
xaxs="i", yaxs="i", # no space around data range
xlab="Easting (m)", ylab="Northing (m)")
image(AF_rgb, add=TRUE) # add the georeferenced image, and
box() # re-draw the box in case of overlap
# plot the points, symbols varying by Year:
# 1. first black unfilled to create 'shadow' behind for better contrast...
points(st_coordinates(afsREE), pch=c(1,0,5,2)[afsREE$Year], col=10, lwd=2,
cex=c(1.7,1.6,1.6,1.6)[afsREE$Year])
# 2. then overplot with white border.
points(st_coordinates(afsREE), pch=c(21:24)[afsREE$Year], col=1, lwd=1.5,
bg=c(2,4,6,8)[afsREE$Year], cex=c(1.5,1.4,1.4,1.4)[afsREE$Year])
# double plot north arrow with small offset to create shadow behind
addnortharrow(pos="topright",padin = c(0.22,0.22),
text.col = 10, border = 10, scale=1.4)
addnortharrow(pos="topright",padin = c(0.2,0.2),
text.col = 1, border = 1, scale=1.4)
addscalebar(plotepsg=32750, pos="bottomleft",linecol = 1,label.col = 1,
padin = c(0.22,0.18),htin = 0.2, label.cex = 1.5, widthhint = 0.15)
# add legend for map image and projection information
legend("topleft", title=expression(bold("Ashfield Flats Reserve")),
legend=c("Photo map source: NearMap Feb 2023 ",
"EPSG: 32750",
"(UTM Zone 50 S, WGS84)"),
box.col="white", bg="#ffffffd0", inset=c(0.01,0.01),
title.cex = 1.4, cex=0.9, y.intersp=0.9)
# add legend to identify points by year
legend("bottomright", title=expression(bold("Year")),
legend=levels(afsREE$Year), text.col = 1, pch=c(21,22,23,24),
pt.bg=c(2,4,6,8), col=1, box.col=1, pt.lwd=2, pt.cex=c(1.6,1.4,1.4,1.4),
bg = "#707062",inset=c(0.03,0.1), cex=1.2, y.intersp = 1)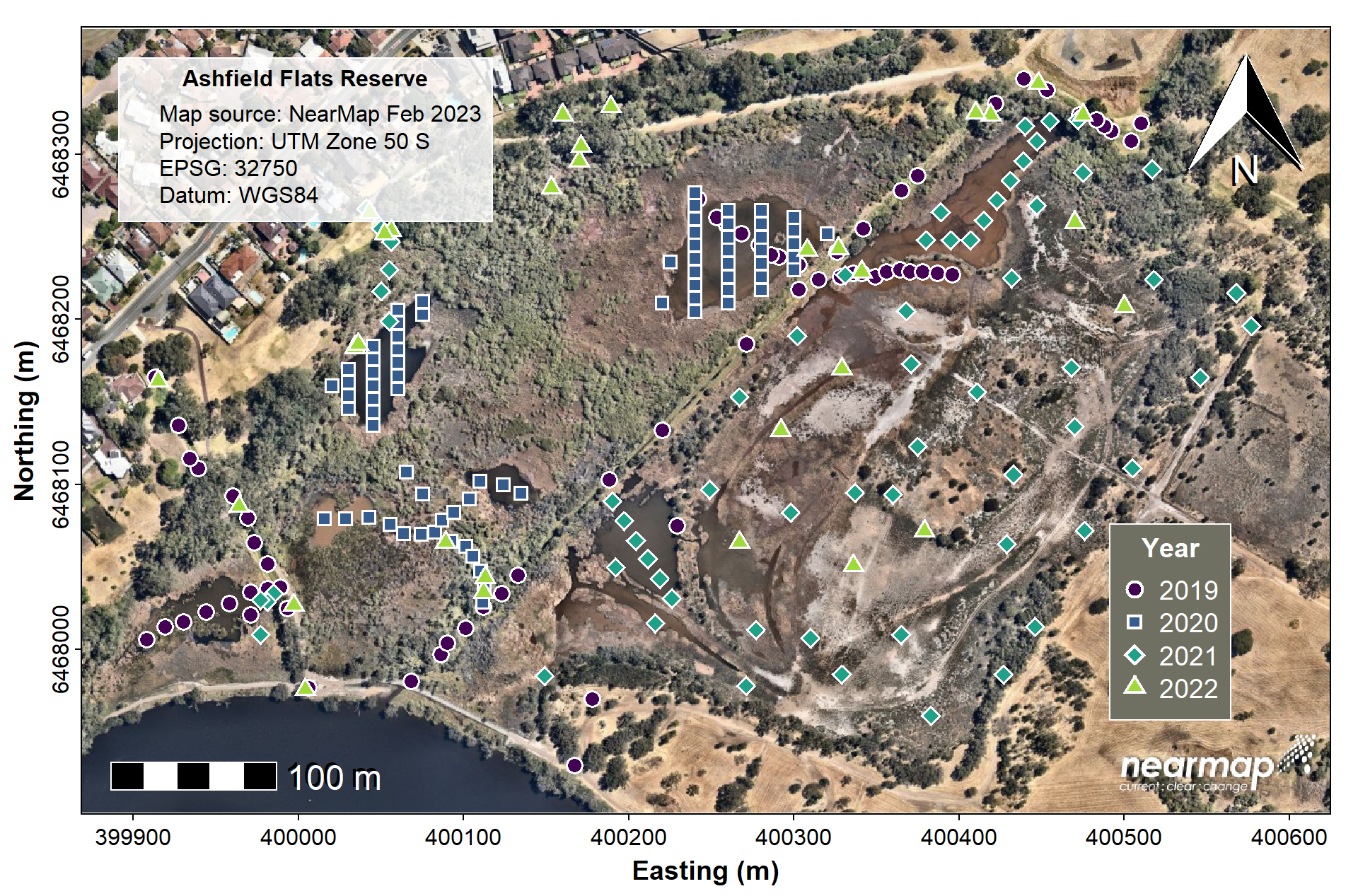
Figure 1: Map of sampling locations at Ashfield Flats Reserve from 2019-2022 plotted on a Nearmap spatial raster.
For comparison we can also use the add.geom = argument
in the image() or plot() function as an
alternative way to plot the points.
palette(c("white",plasma(8, alpha=0.7, beg=0.4), "black","transparent"))
par(mar=c(3,3,1,1), oma=c(0,0,0,0), mgp=c(1.7,0.3,0), tcl=0.25,
lend="square", ljoin="mitre", font.lab=2)
plot(matrix(st_bbox(AF_rgb), nrow=2, byrow=T), asp=1, type="n",
xaxs="i", yaxs="i",
xlab="Easting (m)", ylab="Northing (m)")
# note use of add.geom=... in image() function
image(AF_rgb, add=TRUE,
add.geom=list(afsREE, col=10,
pch=c(21:24)[afsREE$Year],
bg=c(3,5,7,9)[afsREE$Year],
cex=c(1.6,1.4,1.4,1.4)[afsREE$Year]))
box()
addnortharrow(pos="topright",padin = c(0.22,0.22),
text.col = 10, border = 10, scale=1.4)
addnortharrow(pos="topright",padin = c(0.2,0.2),
text.col = 1, border = 1, scale=1.4)
addscalebar(plotepsg=32750, pos="bottomleft",linecol = 1,label.col = 1,
padin = c(0.22,0.18),htin = 0.2, label.cex = 1.5, widthhint = 0.15)
# add legend for map image and projection information
legend("topleft", title=expression(bold("Ashfield Flats Reserve")),
legend=c("Photo map source: NearMap Feb 2023 ",
"EPSG: 32750",
"(UTM Zone 50 S, WGS84)"),
box.col="white", bg="#ffffffd0", inset=c(0.01,0.01),
title.cex = 1.4, cex=0.9, y.intersp=0.9)
# add legend to identify points by year
legend("bottomright", title=expression(bold("Year")),
legend=levels(afsREE$Year), text.col = 1, pch=c(21,22,23,24),
pt.bg=c(3,5,7,9), col=10, box.col=1, pt.lwd=1, pt.cex=c(1.6,1.4,1.4,1.4),
bg = "#606054c0",inset=c(0.03,0.1), cex=1.2, y.intersp = 1)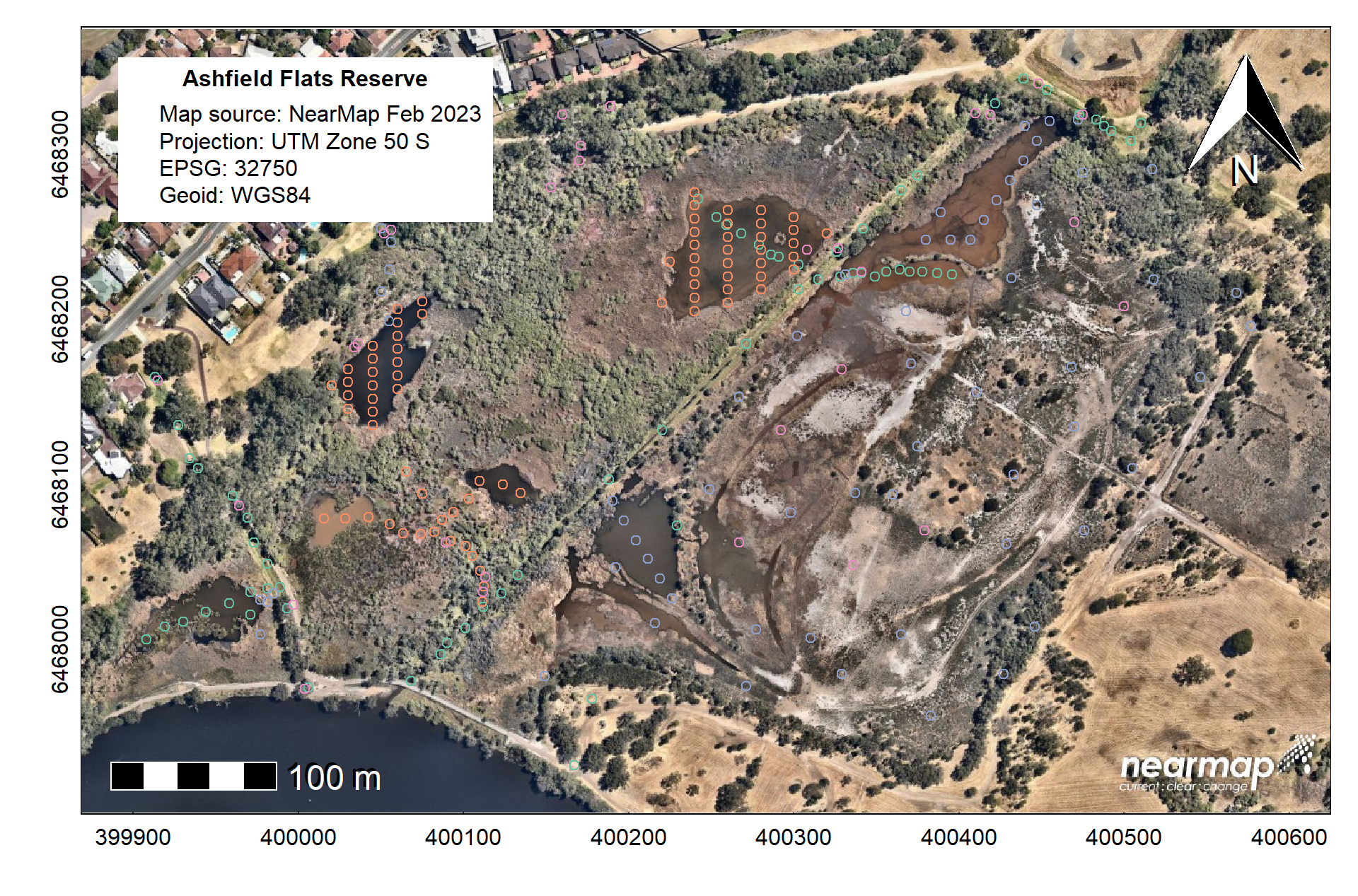
Figure 2: Map of sampling locations at Ashfield Flats Reserve from
2019-2022 plotted on a Nearmap spatial raster using
plot.geom as an argument to image().
The result is similar to adding points separately using
points(), but we have somewhat less control over plot
appearance. We could also add our data in a way that shows values of a
variable, as described in the page on maps in
R.
Packages
Bivand R, Keitt T, Rowlingson B (2022). rgdal: Bindings for the 'Geospatial' Data Abstraction Library. R package version 1.6-2, https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rgdal.
Dunnington D (2022). prettymapr: Scale Bar, North Arrow, and Pretty Margins in R. R package version 0.2.4, https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=prettymapr.
Garnier S., Ross N., Rudis R., Camargo A.P., Sciaini M., and Scherer C. (2021). Rvision - Colorblind-Friendly Color Maps for R. R package version 0.6.2. https://sjmgarnier.github.io/viridis/
Hijmans R (2022). raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling. R package version 3.6-11, https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster.
Pebesma, E., 2018. Simple Features for R: Standardized Support for Spatial Vector Data. The R Journal 10 (1), 439-446, https://doi.org/10.32614/RJ-2018-009
Pebesma E (2022). stars: Spatiotemporal Arrays, Raster and Vector Data Cubes. R package version 0.6-0, https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=stars.
CC-BY-SA • All content by Ratey-AtUWA. My employer does not necessarily know about or endorse the content of this website.
Created with rmarkdown in RStudio using the cyborg theme from Bootswatch via the bslib package, and fontawesome v5 icons.